What is LLM?
Large Language Models (LLMs) are advanced AI systems designed to understand and generate human-like text by processing vast amounts of data. These models, built on architectures like transformers, enable machines to perform a variety of tasks related to natural language understanding and generation, such as translation, summarization, and content creation. The core capability of LLMs lies in their ability to understand context from the input text, voice, or image prompts and produce relevant and coherent responses. As a central component of generative artificial intelligence, LLMs are continually evolving, with significant contributions from leading tech entities like Google, OpenAI, Amazon, and Meta. This project seeks to identify the most effective LLM for specific tasks by evaluating various models through benchmarking and exploratory data analysis. Using data sourced from research papers, model repositories, and performance reports, the analysis aims to simplify the model selection process, ensuring users can find the most suitable LLM quickly and efficiently.
Furthermore, this investigation will forecast the longevity and responsiveness of these models based on historical data and other variables. Through this study, we expect to gain insights into the efficiency and scalability of different LLM architectures, which will assist in the development of more effective and resource-efficient generative AI models. The comparison of open-source and proprietary models will also be a significant aspect of this research, helping to demystify the strengths and weaknesses of each approach in real-world applications.
How LLMs Work
Large Language Models (LLMs) operate by leveraging deep learning techniques, primarily utilizing vast neural networks to process and understand large datasets of text. These models are trained on diverse corpuses of text sourced from books, articles, and the internet, enabling them to learn language patterns, syntax, and semantics. The foundation of LLMs lies in the transformer architecture, which allows the models to weigh the importance of different words in a sentence, regardless of their position, through a mechanism known as attention. This feature enables LLMs to generate responses that are contextually relevant and linguistically coherent.
In practical applications, LLMs take input in the form of text prompts and produce outputs based on the patterns and knowledge they have acquired during training. They can be fine-tuned for specific tasks such as translation, summarization, and question-answering, adapting their outputs to fit the nuances of the particular application. This adaptability makes them highly valuable for developing AI-driven applications across various industries, including healthcare, finance, and customer service, where they can assist in automating responses and generating insights from data.
The effectiveness of an LLM significantly depends on the model's architecture, the quality and diversity of the training data, and the specificity of the tuning for targeted tasks. Understanding these elements is crucial for deploying LLMs effectively, as it helps pinpoint the most suitable model for a given application, ensuring that the technology not only performs optimally but also aligns with the user's or enterprise's specific needs and ethical guidelines.
How to Chose the Best Model
Comparing Large Language Models (LLMs) is essential to understanding their relative strengths and weaknesses, which is crucial for deploying the most effective model for specific tasks. In the rapidly evolving field of AI, different models offer varying degrees of proficiency in processing language, understanding context, and generating human-like text. By benchmarking these models against one another, data scientists and AI engineers can identify which models excel in particular domains, such as healthcare for diagnosing and providing medical recommendations, or finance for predicting market trends and managing customer interactions.
Furthermore, this comparative analysis helps in understanding the trade-offs between model accuracy, processing time, and resource consumption. Businesses can leverage this information to make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and strategic goals. For academia, such comparisons can highlight advancements and gaps in current AI technologies, fostering further research and development. For the open-source community, understanding which models perform best under different conditions can guide contributions towards enhancing model robustness and versatility. Ultimately, the goal of this project is to democratize the understanding of LLM capabilities, enabling users from various sectors to implement AI more effectively and ethically in their operations.
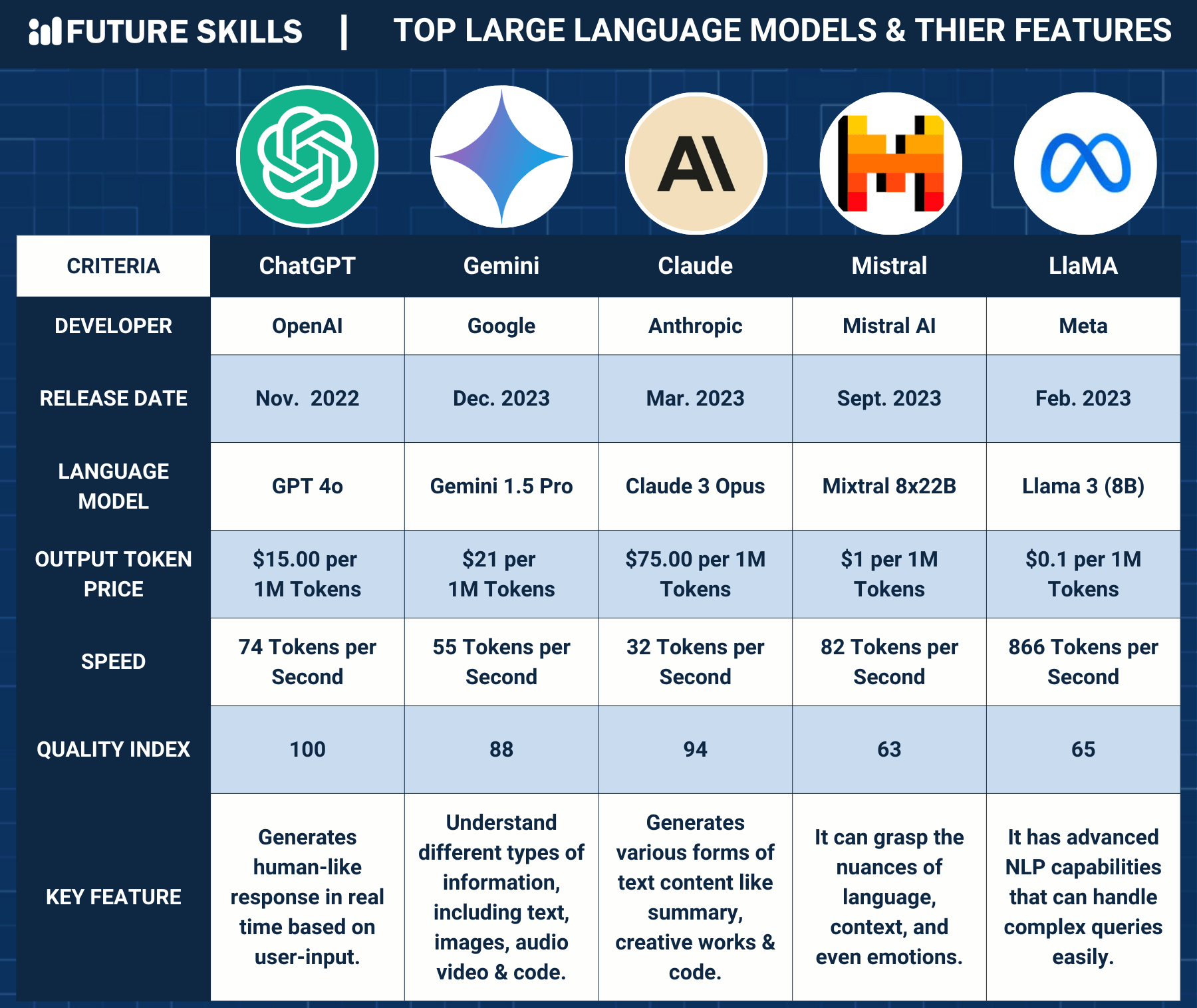
LLM Model Comparison
Despite existing tools and methodologies to compare popular Large Language Models (LLMs), there remains a need for a more predictive and reliable system. Our project addresses this by systematically identifying and analyzing performance metrics of various LLMs across numerous benchmarks, including complex datasets that detail model architectures and training parameters, which are often poorly structured. Traditional analyses have often fallen short in comparing essential aspects such as efficiency, accuracy, scalability, model size, and token size. Additionally, the language-dependent capabilities of LLMs, crucial for their real-world application, have not been adequately addressed.
Previous studies have sporadically tested models on a range of generative AI capabilities—such as adversarial robustness, coding proficiency, following instructions, and math and language skills—relying on manual evaluations or subjective metrics that potentially introduce bias and hinder generalizability. Our approach leverages a more systematic, data-driven methodology to evaluate LLMs comprehensively. By doing so, we aim to enhance understanding and insights into each model's performance, thus enabling more informed decisions when selecting the best LLM for specific applications. This refined evaluation will significantly reduce the time and resources spent on executing repeated prompts across different models and provide valuable insights into the optimal choice and application of LLMs.